Common Errors in Human Body Measurements and How AI Can Fix Them

Whether you’re using a tape measure, 3D scanner, or mobile scanning app, the accuracy of body measurements is never a guarantee. Numerous factors can distort results, making it difficult to get consistent, reliable data. This blog explores the top 10 most common measurement errors and how AI technologies are being used to detect, correct, and even prevent them in real time.
Why Accuracy Matters
From virtual fitting rooms to custom orthotics, the success of personalized products depends on accurate measurements. Even a 1–2 cm deviation in key dimensions can:
- Causes misfitting clothes, shoes, or gear
- Reduce the effectiveness of posture correction tools
- Lead to poor diagnostics in health apps
- Affect digital twin accuracy in ergonomic design
Top 10 Common Errors in Body Measurement
- Incorrect Landmark Selection: Confusing the shoulder tip with the deltoid, or the waist with the hip line.
- Inconsistent Pose: Bent knees or raised arms can drastically alter key dimensions.
- Loose or Tight Clothing: Fabric can add or subtract centimeters, especially in girth measurements.
- Lighting Conditions: Shadows or low light confuse 3D scanners and image-based models.
- Hair and Accessories: Loose hair or headwear can distort head and neck dimensions.
- Poor Calibration of Scanning Devices: Uncalibrated depth cameras lead to warped results.
- Background Interference: Cluttered backgrounds may confuse depth perception in photogrammetry.
- Low Resolution or Occlusions: Missing body parts in scans (e.g., hidden limbs) corrupt the dataset.
- Scanner Positioning: Incorrect angle or distance affects symmetry and proportion.
- Manual Tape Measurement Errors: Human parallax error, inconsistent tension, or misreading the scale.
How AI Detects and Fixes These Errors

AI-powered tools can automatically recognize, flag, and sometimes fix these issues:
- Landmark Detection Models: Deep learning algorithms accurately identify anatomical landmarks even with occlusions.
- Pose Normalization: AI corrects asymmetries by standardizing to canonical poses (T-pose, A-pose).
- Clothing Segmentation: Models separate skin from fabric to compute true body girths.
- Lighting Correction: AI enhances low-light or high-shadow scans using image enhancement models.
- Outlier Detection: Statistical models flag unusual proportions (e.g., waist larger than chest) for review.
- Multi-View Fusion: AI combines multiple views into a single accurate 3D model, even from a smartphone.
- Real-Time Feedback: AI assistants guide users with voice prompt, “Please raise your arms” or “Step back 30 cm.”
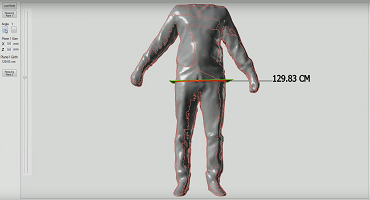
How 3D Measure Up Addresses These Errors
Measurement errors are inevitable, but they’re not unmanageable. With AI in the loop, even low-cost consumer devices can deliver professional-grade accuracy. By understanding the common pitfalls, and how tools like 3D Measure Up are designed to overcome them, you can ensure better outcomes in fashion, fitness, healthcare, and beyond.
3D Measure Up incorporates many of these AI-driven features to ensure users and professionals get clean, actionable data:
- Automated Landmark Detection using ML models trained on thousands of scans.
- Pose Correction Pipelines standardize scanned poses before measurement begins.
- Clothing-aware Measurements distinguish body shape from external obstructions.
- Measurement Validation Engine flags anomalies and suggests rescans or adjustments.
Curious how AI can optimize your measurement pipeline? Explore 3D Measure Up and request a FREE trial today.